NEWS
Understanding High and Low Frequency Transformers: Essential Insights for Electrical Professionals
Release time:
Feb 03,2025
Transformers are vital components in electrical engineering, particularly in power distribution and signal processing. Among them, high and low frequency transformers serve distinct yet crucial roles. Understanding the differences and applications of these transformers is essential for professionals in the electrical and electronics industries.
High frequency transformers are designed to operate efficiently at elevated frequencies, typically above 20 kHz. These transformers are often used in applications such as switching power supplies, RF (radio frequency) amplifiers, and signal processing systems. One of the key characteristics of high frequency transformers is their smaller size and weight compared to low frequency transformers. This is largely due to the reduced core size, which allows for higher magnetic flux densities and minimizes losses. The materials used in the core, such as ferrite, are specifically selected to enhance performance at these frequencies. When designing high frequency transformers, engineers must consider factors like parasitic capacitance and leakage inductance, as these can significantly impact overall efficiency and performance.
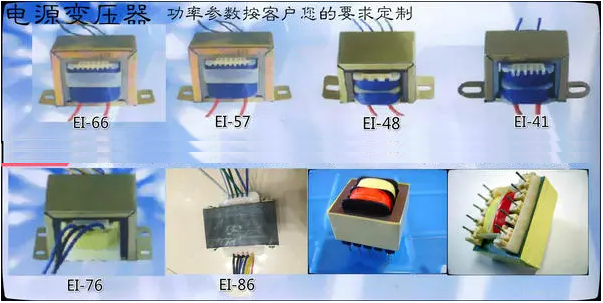
On the other hand, low frequency transformers typically operate at frequencies ranging from 50 Hz to 60 Hz, making them suitable for standard power distribution and electrical devices. These transformers are commonly found in utility companies’ power grids, industrial power supplies, and various household appliances. Low frequency transformers tend to be larger and heavier, utilizing silicon steel cores that are optimized for low-frequency applications. Their design focuses on maximizing efficiency and minimizing losses due to hysteresis and eddy currents. Professionals working with low frequency transformers must pay close attention to their voltage and current ratings, as well as thermal management, to ensure reliable operation in their specific applications.
Both high and low frequency transformers play essential roles in the electrical landscape. High frequency transformers enable advancements in modern technologies, such as telecommunications and renewable energy systems, while low frequency transformers remain the backbone of traditional power distribution networks. Understanding their operational principles, applications, and key differences not only enhances a professional's knowledge but also aids in making informed decisions when selecting the right transformer for a specific project.
In conclusion, mastering the concepts surrounding high and low frequency transformers is crucial for electrical professionals. By recognizing their unique characteristics and applications, one can effectively contribute to designing efficient electrical systems that cater to both contemporary and traditional energy needs.
High frequency transformers are designed to operate efficiently at elevated frequencies, typically above 20 kHz. These transformers are often used in applications such as switching power supplies, RF (radio frequency) amplifiers, and signal processing systems. One of the key characteristics of high frequency transformers is their smaller size and weight compared to low frequency transformers. This is largely due to the reduced core size, which allows for higher magnetic flux densities and minimizes losses. The materials used in the core, such as ferrite, are specifically selected to enhance performance at these frequencies. When designing high frequency transformers, engineers must consider factors like parasitic capacitance and leakage inductance, as these can significantly impact overall efficiency and performance.
On the other hand, low frequency transformers typically operate at frequencies ranging from 50 Hz to 60 Hz, making them suitable for standard power distribution and electrical devices. These transformers are commonly found in utility companies’ power grids, industrial power supplies, and various household appliances. Low frequency transformers tend to be larger and heavier, utilizing silicon steel cores that are optimized for low-frequency applications. Their design focuses on maximizing efficiency and minimizing losses due to hysteresis and eddy currents. Professionals working with low frequency transformers must pay close attention to their voltage and current ratings, as well as thermal management, to ensure reliable operation in their specific applications.
Both high and low frequency transformers play essential roles in the electrical landscape. High frequency transformers enable advancements in modern technologies, such as telecommunications and renewable energy systems, while low frequency transformers remain the backbone of traditional power distribution networks. Understanding their operational principles, applications, and key differences not only enhances a professional's knowledge but also aids in making informed decisions when selecting the right transformer for a specific project.
In conclusion, mastering the concepts surrounding high and low frequency transformers is crucial for electrical professionals. By recognizing their unique characteristics and applications, one can effectively contribute to designing efficient electrical systems that cater to both contemporary and traditional energy needs.