NEWS
Understanding High and Low Frequency Transformers: Essential Insights for Electrical Applications
Release time:
Feb 13,2025
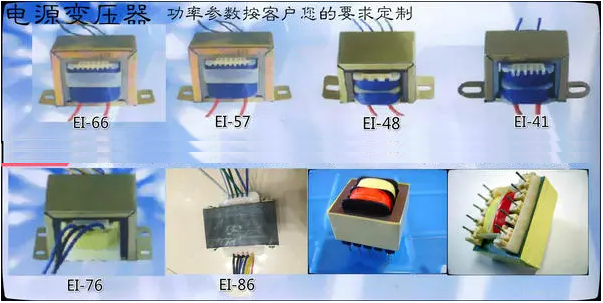
Transformers are vital components in the electrical industry, serving as devices that transfer electrical energy between circuits through electromagnetic induction. Among the various types of transformers, high and low frequency transformers are particularly significant due to their distinct functionalities and applications in different electrical systems.
High frequency transformers are typically designed to operate at frequencies of 1 kHz and above. They are commonly utilized in applications such as switch-mode power supplies, RF amplifiers, and telecommunication devices. One of the key features of high frequency transformers is their compact size, which is a result of the higher frequency operation. This leads to a reduction in the core size and weight, making them suitable for portable and space-constrained applications. Additionally, high frequency transformers tend to have higher efficiency and reduced losses due to the minimization of eddy currents and hysteresis losses in the core material.
On the other hand, low frequency transformers generally operate at frequencies below 1 kHz, with many traditional power transformers falling within this category. They are predominantly used in power distribution systems, industrial applications, and residential electrical systems. Low frequency transformers are typically larger and heavier due to their design, which accommodates lower frequencies. The core material is selected to handle the lower frequency operation, ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Low frequency transformers are crucial for stepping up or stepping down voltage levels, facilitating efficient power transmission over long distances.
Both high and low frequency transformers are designed with specific core materials, including ferrite for high frequency transformers and silicon steel for low frequency transformers. The choice of core material significantly affects the performance characteristics, including efficiency, thermal management, and overall reliability in the application.
Understanding the specifications and applications of high and low frequency transformers is essential for electrical engineers and professionals in the field. It is important to consider factors such as operating frequency, core material, and intended application when selecting the right transformer for a project. By leveraging the unique characteristics of these transformers, engineers can optimize performance, enhance energy efficiency, and improve the overall functionality of electrical systems.
In summary, high and low frequency transformers play critical roles in the electrical industry, each serving distinct applications and needs. By gaining insights into their functionality, professionals can make informed decisions that contribute to the efficiency and reliability of their electrical systems.
High frequency transformers are typically designed to operate at frequencies of 1 kHz and above. They are commonly utilized in applications such as switch-mode power supplies, RF amplifiers, and telecommunication devices. One of the key features of high frequency transformers is their compact size, which is a result of the higher frequency operation. This leads to a reduction in the core size and weight, making them suitable for portable and space-constrained applications. Additionally, high frequency transformers tend to have higher efficiency and reduced losses due to the minimization of eddy currents and hysteresis losses in the core material.
On the other hand, low frequency transformers generally operate at frequencies below 1 kHz, with many traditional power transformers falling within this category. They are predominantly used in power distribution systems, industrial applications, and residential electrical systems. Low frequency transformers are typically larger and heavier due to their design, which accommodates lower frequencies. The core material is selected to handle the lower frequency operation, ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Low frequency transformers are crucial for stepping up or stepping down voltage levels, facilitating efficient power transmission over long distances.
Both high and low frequency transformers are designed with specific core materials, including ferrite for high frequency transformers and silicon steel for low frequency transformers. The choice of core material significantly affects the performance characteristics, including efficiency, thermal management, and overall reliability in the application.
Understanding the specifications and applications of high and low frequency transformers is essential for electrical engineers and professionals in the field. It is important to consider factors such as operating frequency, core material, and intended application when selecting the right transformer for a project. By leveraging the unique characteristics of these transformers, engineers can optimize performance, enhance energy efficiency, and improve the overall functionality of electrical systems.
In summary, high and low frequency transformers play critical roles in the electrical industry, each serving distinct applications and needs. By gaining insights into their functionality, professionals can make informed decisions that contribute to the efficiency and reliability of their electrical systems.